Triton Space Technologies is a Boston, Massachusetts-based engineering design and manufacturing company that specialises in producing rocket propulsion systems. In addition to manufacturing its line of high-pressure fluid system components and propulsion solutions, it provides contract engineering and prototype manufacturing services for customers requiring bespoke products, which it manufactures onsite in its state-of-the-art CNC machine shop.
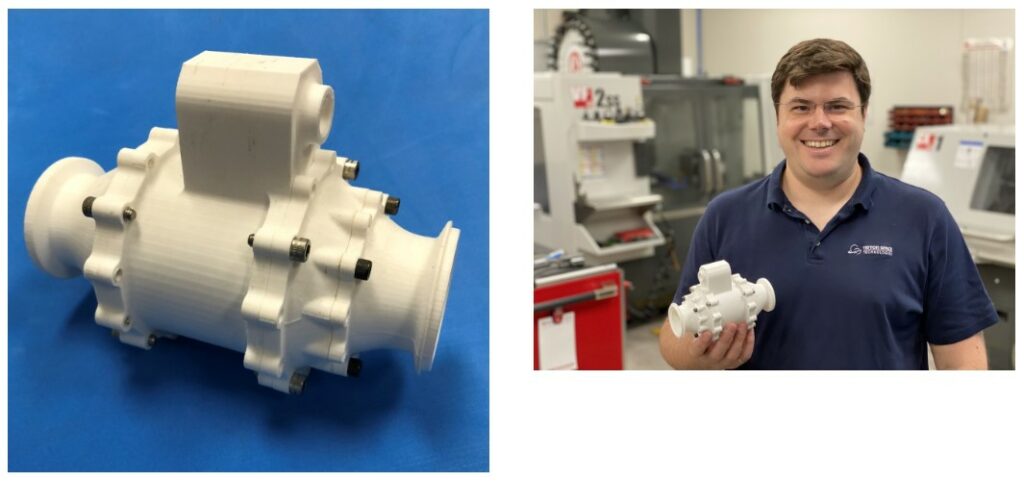
They utilised the MakerBot METHOD X 3D Printer for designing and manufacturing complex rocket engine parts for a lunar landing mission in 2021.
Functionality of the METHOD X 3D Printer: Triton’s President and CEO, Luke Colby, highlighted the precision and reliability of the METHOD X printer in maintaining tolerances required for moving parts in the rocket valves. This precision was unexpected for a desktop 3D printer.
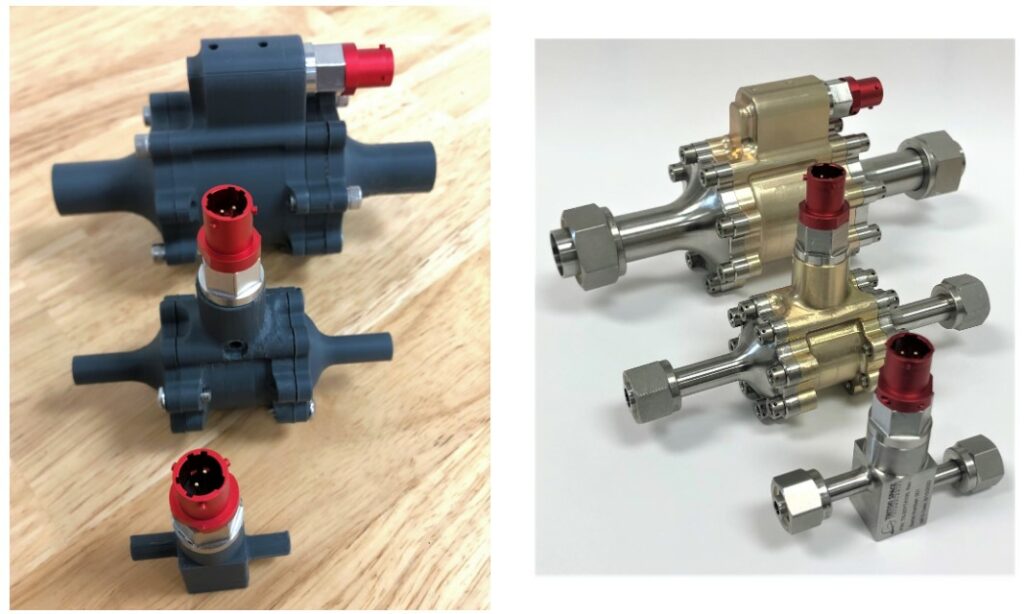
Efficiency in Prototyping: Before using METHOD X, Triton had to machine prototypes from aluminium, which was time-consuming and wasteful. 3D printing with METHOD X significantly reduced prototype development time and material waste.
Complex Geometries with Dissolvable Supports: The use of Stratasys® SR-30 soluble support material allowed Triton to produce functional prototypes with the demanding tolerances required in the aerospace industry. This capability was crucial for creating sophisticated prototypes.
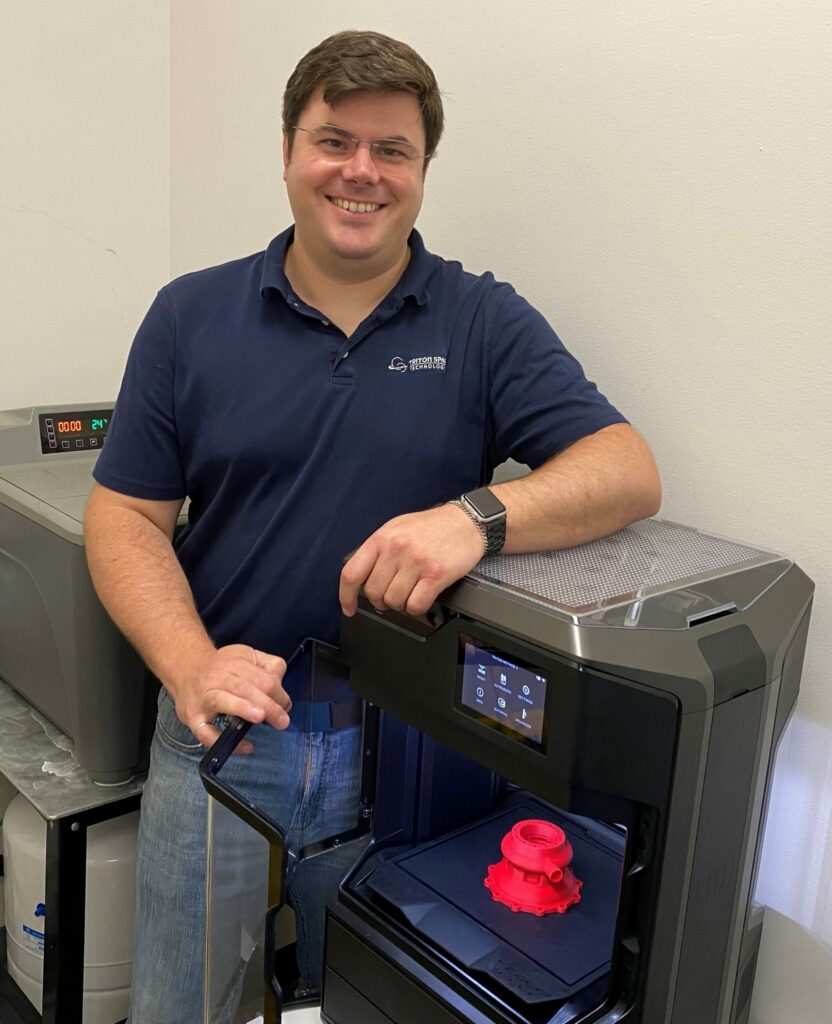

Material Advantages: The capability to print with durable, engineering-grade ABS and the potential of using MakerBot Nylon Carbon Fiber was noted as a significant benefit. The flexibility in materials allows for continual improvement and adaptation in their manufacturing processes.
Modularity and Material Expansion: Colby emphasized the importance of the METHOD X printer’s modularity, allowing for future improvements and adaptability in material usage. This aspect is critical for keeping up with the rapid pace of technological advancements.