Big Bang Upgrade: Up to 30% Trade-in Discount
Limited Time Offer: SAVE with METHOD X and METHOD XL Bundles.
- 3D Printers
- 3D Printers
- FDM
- Polyjet
- Metal
- Ceramic
- DLP
- SAF
- View all
- Professional Entry Solutions
- Large Team Solutions
- Carbon Filled Solutions
- Production Solutions
- Professional Entry Solutions
- Production Solution
- Medical & Dental Solutions
- Professional Entry Solutions
- Medium Size Production
- Large Size Production
- Entry Level Ceramics
- Advanced Ceramics
- DLP 3D Printer
- SAF 3D Printer
- 3D Scanners
- 3D Scanners
- Large Parts with Big Data Sets
- Small Parts with High Accuracy
- Fully Mobile Scanning
- Large Parts with Big Data Sets
- Small Parts with High Accuracy
- Fully Mobile Scanning
- Long-Range Scanning
- Materials
- High Performance Materials
- View All
- Industries
- ApplicationApplications
- Manufacturing
- Rapid Prototyping
- SoftwareSoftware
- Data Prep and STL Editor
- Design Optimisation for AM
- Slicing Software
- Work Order Management
- Manufacturing On Demand
Manufacturing On Demand
Solutions
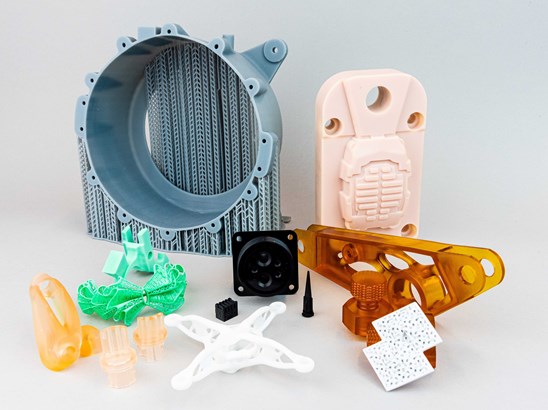
























































 For functional prototypes and mechanical parts, ABS is a popular choice. It is a petroleum-based plastic known for its excellent durability, impact resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures. Additionally, ABS can be easily fabricated, glued, and painted, making it an ideal choice for product housings, automotive components, and various consumer goods.
For functional prototypes and mechanical parts, ABS is a popular choice. It is a petroleum-based plastic known for its excellent durability, impact resistance, and ability to withstand high temperatures. Additionally, ABS can be easily fabricated, glued, and painted, making it an ideal choice for product housings, automotive components, and various consumer goods.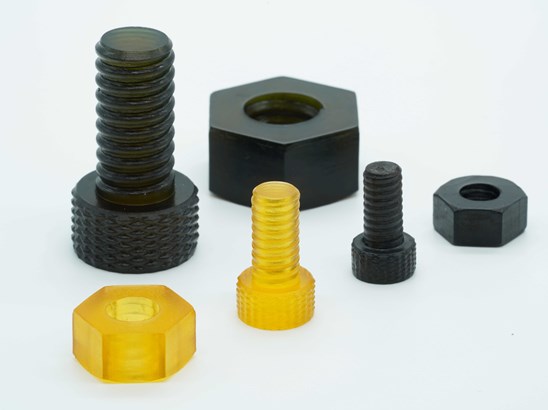 Nylon is an all-around powerhouse material, offering both fantastic strength and remarkable flexibility. Its durability, resistance to fatigue, and low friction coefficient make it an ideal choice for functional parts, gears, hinges, and various moving parts. Nylon is also resistant to chemicals and UV light, further increasing its diverse range of applications.
Nylon is an all-around powerhouse material, offering both fantastic strength and remarkable flexibility. Its durability, resistance to fatigue, and low friction coefficient make it an ideal choice for functional parts, gears, hinges, and various moving parts. Nylon is also resistant to chemicals and UV light, further increasing its diverse range of applications.



